February 19, 2023
by Stephen Stofka
When analyzing the economies of some developing countries, economists refer to a “resource curse,” a commodity like oil or minerals that a country can sell on the global market. In a developing country, that commodity may become the main source of foreign currency, used to pay for imports of other goods. The extraction of that resource requires capital investment which usually comes from outside the country. If the production of that resource is not nationalized, most of the profits leave the country.
There are a few big winners and a lot of losers. This uneven ratio promotes economic and social inequality. Political instability arises as people within the country want to get a hold on those resources. Some politicians promise to use the profits from the resource to benefit everyone but those who seize power benefit the most. Political priorities determine economic decisions and the production of that resource becomes inefficient.
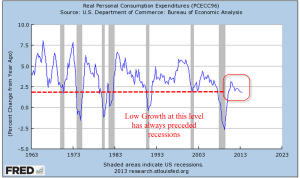
A key factor in the “resource curse” is that its contribution to GDP is usually far above its contribution to employment. If a mining sector accounts for 2% of employment but contributes 10% to GDP, the ratio of employment / GDP % equals 2%/10%, or 0.2. Ratios that are far below 1 do not promote a healthy economy. Industries that are closer to a 1-1 ratio will produce a more well rounded and vibrant economy because employed people spend their earnings in other sectors of the economy – a diffusion effect. Some economists might say that a low ratio means that capital is being used more efficiently and attracts capital investment. However, that efficiency comes at an undesirable social and economic cost.
Let’s look at some examples in the U.S. The construction industry contributes 3.9% to GDP (blue line in the graph below) but accounts for 5.1% of employment (red line). Notice that this is the opposite of the example I gave above. The 1.31 ratio of employment/GDP is above 1, meaning that the industry employs more people for the direct value that it adds to the economy. Construction spending includes remodels and building additions but does not include maintenance and repair (Census Bureau, n.d.). In the chart below, look at how closely GDP and employment move together. The divergence in the two series since the pandemic indicates the distortions in the housing market because of rising interest rates. Builders have put projects on hold but employment in the sector is still rising because of the tight labor market.

The finance sector’s share of the economy has grown since the financial crisis yet employment has remained steady – or stuck, depending on one’s perspective. The great financial crisis put stress on banks, big and small, but the government bailed out only the “systemically important” banks, leaving smaller regional banks to fend for themselves. The larger banks absorbed many smaller banks, leading to a consolidation in the industry. That consolidation and investments in technology helped the sector become more efficient. The ratio is about 0.75, above the 0.2 ratio in the example I gave earlier. I labeled the lines because the colors are reversed.

Retail employs a lot of people relative to its contribution to GDP. The ratio is about 1.65. Does that mean retail is an inefficient use of capital? Retail sales taxes pay for many of the city services we enjoy and take for granted. Retail is the glue that holds our communities together.

The manufacturing sector employs fewer people in relation to its GDP contribution. It’s ratio is 0.77, about the same as finance.

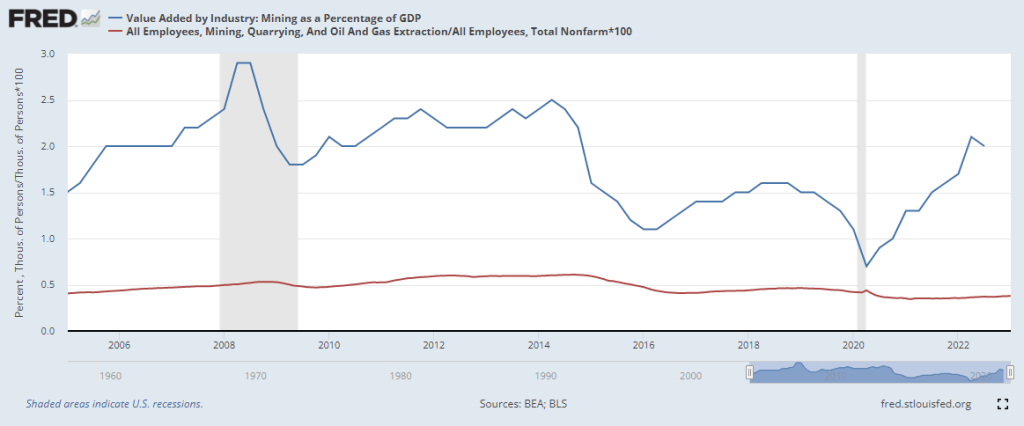
As I noted earlier, the mining sector is capital intensive with a high ratio of GDP to employment. This sector includes gas and oil extraction. In the U.S. that ratio averages about 0.33 but it is erratic global demand. Look at the effect during the pandemic. In our diversified economy, the mining sector contributes only a small amount, like 2%. In a developing country like Namibia in southern Africa, mining accounts for 10% of GDP. In the pandemic year, the demand for minerals declined and Namibia’s economy fell 8%.
Lastly, I will include the contribution of health care, education and social services, which contribute 7.5% to GDP but employ almost a quarter of all workers. Since the financial crisis and the passage of Obamacare, this composite sector contributes an additional 1% to GDP. These sectors include many public goods and services that form the backbone of our society. The 3.0 ratio is the inverse of the mining sector.

To summarize, the construction, retail, health care and education sectors have a ratio above 1. They employ more people for each percentage unit of output. The finance, manufacturing, mining, oil and gas sectors have ratios less than 1, employing fewer people per percentage unit of output. For readers interested in the GDP contribution of other industries, the Federal Reserve maintains a list of charts, linked here [https://fred.stlouisfed.org/release?rid=331].
//////////////////
Photo by Camylla Battani on Unsplash
Census Bureau. (2019, April 15). Construction spending – definitions. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 16, 2023, from https://www.census.gov/construction/c30/definitions.html
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Value Added by Industry: Construction as a Percentage of GDP [VAPGDPC], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/VAPGDPC, February 12, 2023.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, All Employees, Construction [USCONS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/USCONS, February 12, 2023.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, All Employees, Total Nonfarm [PAYEMS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/PAYEMS, February 12, 2023.
I will not do a complete reference for each series. Here’s the identifiers for each series: Finance Value Added – VAPGDPFI. Employment in finance – USFIRE. Construction employees – USCONS. Retail Value Added – VAPGDPR. Retail Employees – USTRADE. Manufacturing Value Added – VAPGDPMA. Manufacturing Employees – MANEMP. Education, Health Care, Social Services Value Added – VAPGDPHCSA. Employment is a composite of 4 series. Mining Value Added – VAPGDPM. Mining Employment – CES1021000001