September 10, 2023
by Stephen Stofka
This week’s letter is about the mix of full-time and part-time workers and what it tells us about the economy. Although unemployment remains below 4%, it rose slightly, according to the most recent unemployment report. This was a good sign, however, because much of that increase was due to formerly discouraged people returning to the labor force and looking for a job. This economy is producing historic employment numbers. Let’s dig in.
I’ll be looking at ratios of workers to the working age population so I’ll discuss that briefly before heading into the data. The Bureau of Labor Statistics now defines the working age population as someone 16 years and older. According to that definition, a 90 year old person is working age. The U.S. is part of the OECD group of developed countries, which uses a more traditional definition of the working age population as 15 to 64. I am going to use the OECD definition to make historic comparisons more accurate. Two-thirds of this working age population is employed full or part time.
The percent of working age people who are employed full time – the red line in the chart below – is about 64%, a historic high that has eclipsed the economic boom of the late 1990s.

Only 2% of working age people are working part time.

The ratio of full-time workers to part-time workers reveals the strength of the economy. When it is high, employers have the confidence to commit resources to full-time workers, including better benefit packages. Workers have more bargaining power. The chart below shows the peaks in that ratio since the 1960s. A rise in investment accompanied each period. Defense spending led the surge in the 1960s. Investment in technology was a major driver of emploment growth in the 1990s. Spending on infrastructure has been a key driver of growth since the pandemic.

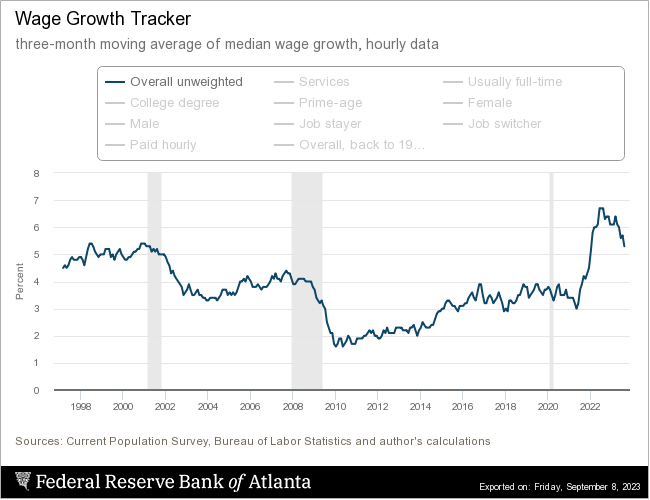
In the post-pandemic recovery, employers have sharply increased wages to fill positions, as shown below by the Atlanta Fed’s wage growth tracker. The decrease in wage growth during the past year is more typical of recessions but without a recession. In the chart below, note that today’s wage growth is one percent higher than the peak during the strong labor market of the late 1990s.
The greater the number of full-time workers, the more the federal government receives in FICA taxes, reducing the yearly deficit in the Social Security Trust Funds. Since the early 1980s, income tax rates have been indexed to inflation but social security taxes have not. Only the earnings subject to social security, the earnings cap, is indexed. According to the latest Trustees report, the drain on the trust fund last year was $22 billion, less than 1% of the $2.8 trillion fund, but a drain, nevertheless. The first of the historically large Boomer generation were eligible for retirement almost a decade ago. The last of that generation will be eligible for retirement in eight years. The era of annual surpluses in the trust funds is over. During the past decade, outlays increased at a 4.5% annual pace while tax collections increased at a 5.3% rate. This was a welcome change of pace from the previous decade 2003 through 2012 when social security tax collections grew at only 3.6% annually, while outlays grew at a 5.4% rate.
The financial crisis had a deep negative impact on the trust funds and the current estimate is that the trust funds will be depleted in 2034. After that date, retirees will not receive full benefits without some legislation to provide additional funding. In 1990, the trustees estimated a depletion date of 2043, almost nine years later than today’s estimate. These long-range forecasts necessitate many assumptions about economic growth and benefits and such forecasts cannot anticipate outlier events like the financial crisis. There is a lot of catching up to do. We need all the boom we can get.
/////////////////
Photo by bruce mars on Unsplash
Keywords: social security, taxes, employment, wages
Note: In the past twenty years, the number of working Americans who are older than 65 has jumped from four million to 11 million, or 6.5% of the labor force.
