June 16, 2024
This week’s letter continues my study of expectations, focusing on the political aspect. While some economists have treated expectation and anticipation as synonyms (the Stockholm school, for one), I want to distinguish between the two. Expectation is planning for or projecting into the future from an observation point in the present. Anticipation is visionary, an imaginative leap into the future in which some event or state has already happened. Anticipation is intuitive; expectation is calculating.
Anticipation invokes our identity and biases as well as our imagination. Political campaigns often target our sense of anticipation with negative advertising that impugns the candidate, then implies that a vote for such a character is an association with that candidate. Imagine how bad things would be if such a person were elected. Do we really want to be associated with someone like that? At a 2008 Presidential debate between Republican candidate John McCain and Democratic candidate Barack Obama, McCain defended Obama’s character against the innuendo spread by right wing TV and talk radio personalities. Much as we deplore negative political advertising, it is effective.
In the game of chess, each player strategizes to take the other’s king. Getting to the other side of the board first does not win the game. One achieves victory by the opponent’s loss. Elections like those in the U.S. are similar to baseball or football. Preventing the opposing team from scoring will not win the game. The victorious team must also make a score. The winner must get more points than the loser, a typical characteristic of a race, which is why our type of elections are called first past the post voting. What makes an election different than a 100-yard dash are the battle tactics employed to weaken an opponent’s efforts to score votes. Successful campaigns strive to get there first while persuading voters to vote NO on their opponent. Campaigns target two separate processes we use to make choices.
One axiom of rational choice theory in economics is a completeness of preferences – that people are able to weigh the costs and benefits of two options and choose the option that maximizes their self interest. We choose an option that provides what we think will give us the most utility. Yes, we make mistakes, but the errors are random. Behavioral economists have challenged the assumption that our choices are rational, pointing out biases that introduce systemic, not random, error in our choices. Losses have a greater impact on our senses than equal gains. Options may be too complex to evaluate fully before making a choice, so we rely on instinct.
In Chapter 8 of his book, Optimally Irrational, Lionel Page (2023) discusses the debate and presents several examples that test the axiom. Given two grocery lists, could you pick the best option? Consider there might be twenty or more items on the list and a grocery store carries thousands of items. How could any person decide the best option? This past week, after checking out my groceries, I picked up what I thought was the receipt that had fallen out of my pocket. With a glance, I knew it was not mine because there were a few items on the list that I would never buy. I realized then that I could choose between two random grocery lists in less than a minute. I would scan the list for things that I definitely did not like or want. The list that had the fewest of those would be my choice.
When we do have difficulty making choices, it is because we are trying to choose the best, not the worst, option. Page cited (p. 101) an episode of the Big Bang Theory where Sheldon had difficulty choosing between two computer game consoles. He had approached the problem in a very analytical manner typical of Sheldon and was unable to choose. The shortcut, or heuristic, of decision-making that we use in our daily lives is not finding the best, but establishing the worst of two options. We know our dislikes more than our likes because our dislikes amplify the cost of our decisions, helping us choose the cheaper option with less deliberation. Secondly, identifying the worst alternative makes it more probable that we can live with our decision.
A successful political campaign structures its rhetoric to take advantage of this shortcut in decision making. Just before the 1980 election, candidate Ronald Reagan posed a question to President Carter at an October debate: Are you better off than you were four years ago? Despite the word “better” in the question, this was an “identify and reject the worst” choice using both rational expectations and more imaginative anticipations. On the one hand were the empirical realities of high inflation and unemployment, and the energy shortages that voters had experienced during Carter’s term. Voters could form expectations based on that data. Reagan’s term as Governor of California during the 1960s gave voters some basis to form a rational expectation of a Reagan term. However, much was left to voters’ imaginations to construct a post-hoc, or after the fact vision of a Reagan term. This was the anticipation instinct at work. The question helped turn a close race into a landslide victory for Reagan.
Some voters may not have a clearly defined worst or judge two candidates to be equally worse. Each may have one or two repulsive personal characteristics, political alliances or policy stances. To appeal to those voters, a political campaign offers hope that their candidate will maximize a voter’s income, personal freedom, autonomy or other circumstance like the health of the community a voter lives in. The negative approach targets the cost calculation that voters make. The positive approach appeals to the benefit calculation, but the negative approach is the more powerful. The disadvantage of the negative approach is that it can persuade voters to abstain from voting. In a national campaign for President, a voter’s abstention is neutral, but a lack of turnout can be a decisive factor in local races where a small number of voters can be the tipping point of a political victory.
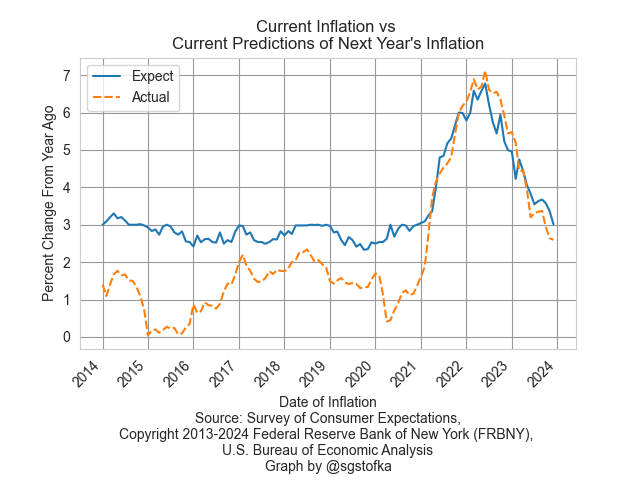
I hope I have made a clear distinction between expectations and anticipations. When a person stands in the present and plans ahead for some state or event, she is expecting. When a person stands in an imagined future and looks back at an event, she is anticipating. I will take a closer look at the unintentional political alliances between voters as a result of the symbiosis between expectations and anticipations.
/////////////////////
Photo by Ahmed Almakhzanji on Unsplash
Keywords: campaign, election, choice, anticipation, expectation
Page, L. (2023). Optimally irrational: The good reasons we behave the way we do. Cambridge University Press.