June 8th, 2014
This week I’ll look at some long term trends in the labor market, short term economic indicators and an unusual move by the European Central Bank.
**************************
May Labor Report
On Friday, the BLS reported job gains of 217K, in line with expectations. The big headline is that we have finally recovered all the jobs that were lost during the recession.
That headline obscures the weakness in the recovery of the labor market. The number of jobs gained comes from the monthly survey of businesses. The household survey shows that the economy is still short about 1 million jobs from its mid-2007 high. A million jobs is less than 1% of the workforce but we’ll see in a minute that the household survey may be giving us a truer sense of the labor market. Like a fighter who has been knocked down a few times, the labor market is back on its feet but still maintains a defensive posture.
The number of involuntary part-time workers, those who want full time work but can’t find it, has declined in small increments over the past few years but remains stubbornly high. Gone are the upward spikes in part-time employment, indicating that the labor market is at least more predictable.
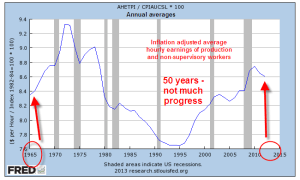
7.3 million involuntary part-timers is about 2.3 million more than a more normal level of 5 million. Half of that number means that there are effectively 1.2 million jobs still “missing.” Add to that 1.2 million or more jobs needed each year just to keep up with population growth. 1.2 million x 6 years = 7.2 million. Add in the 1.2 million jobs to reduce part-timers to normal levels and that is 8.4 million jobs still missing. Let’s deduct a million jobs or so that were gained before the recession because of an overheated housing market and we still have a 7.5 million jobs gap, or 5% of the potential workforce. As I will show next week, this job gap puts downward pressure on wages, on personal income, on consumer demand, on…well, just about everything.
This month marked the fourth month in a row that job gains have been higher than 200K. Two of those four months of consistently strong job gains came during a weak quarter of economic growth and particularly weak corporate profit growth. More on that next week.
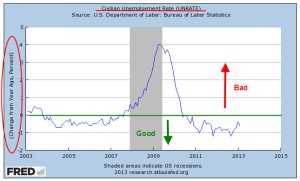
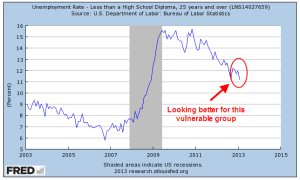
The narrow measure of unemployment remained unchanged at 6.3% but the widest measure, the U-6 rate, continues to decline from a high of (gulp!) 17% to a current level of 12.2%.
The number of long-term unemployed edges downward.
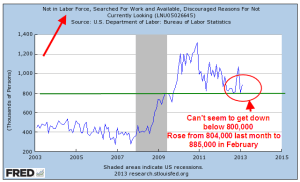
Although there is much variation in the monthly count of people who are classified as discouraged, the trend is downward from the hump in 2011 and 2012.
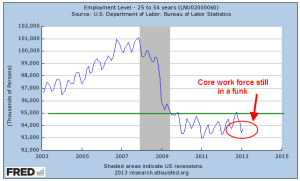
After breaking above the 95 million mark earlier this year and rising, the number of workers aged 25 – 54, what I call the core work force, has declined back toward the 95 million mark.
According to the monthly survey of businesses, half of all employees are women. My gut instinct tells me that this is more out of necessity than desire. Women do what they have to do to meet the needs of their families and many of those jobs may be part-time to accommodate family needs.
The decline in male-dominated employment in the manufacturing and construction sectors can be seen in the declining participation rate of men in the work force.
Earlier in the week, ADP reported private job gains of 180K, below the consensus estimate of 210K. A graph of the past decade shows that private job growth has steadied during the past year.
We should probably keep this longer-term perspective in mind to balance out the monthly headlines. Zooming in on the past few years shows the dips, one of which was the recent winter lull. The trick is to keep a balance between the short-term and the long-term.
The market is expecting growth this quarter that will offset the winter weakness and will probably react quite negatively if prominent indicators like employment, auto sales or housing should disappoint.
Over 10,000 boomers a day reach retirement age. Not all of them retire but some back of the envelope estimates are that 100K or more do drop out of the labor force each month. For the past eight months or so, new entrants and re-entrants into the job market has offset these retirees and the number of people not in the labor force has leveled off in the range of 91 to 92 million.
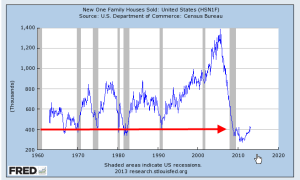
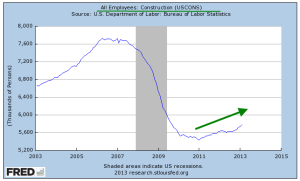
Construction employment finally crossed the psychological 6 million mark this month and for the past year or so has been on the rise from historic lows. As a percent of the work force, however, employment in this sector is near all-time lows. Let’s zoom out and look at the past fifty years to get some perspective on this sector. A more normal percentage of the work force would be about 5%. The difference is 1 to 1.2 million jobs “missing” in a sector which pays better than average.
In summary, there is a lot to like in the labor reports of the past few months. But we should not kid ourselves. The long-term trends show that the challenges are steep. The question is not whether the glass is half empty or half full. The question is how many small holes there are in the bottom of the glass.
*********************
Central Banks
Helping to fuel the upward climb in the market this week was the message that central banks are willing to adopt whatever policies they can to support the economy. In response to the threat of deflation in the Eurozone, the European Central Bank (ECB) made an unprecedented move this week, charging banks 1/10% to park their excess reserves with the central bank. What does this mean? Customary policy is that member banks must keep on deposit with the central bank a certain percentage of their outstanding loans and other securities to guard against losses. For larger banks, this is about 10%. In a simple example, let’s say that a bank makes another loan for $100. It must keep an additional $10 on deposit with the central bank. Let’s say it already has $12 extra on deposit with the central bank. The central bank would then pay interest to the bank for the extra $2. The policy change this week by the ECB reverses that policy: member banks must now pay the central bank for any excess reserves. Essentially the central bank is charging banks for not making more loans, a policy which some monetary economists have encouraged the Federal Reserve to adopt.
**********************
CWPI (Constant Weighted Purchasing Index)
On Monday, the Institute for Supply Management released their monthly survey of purchasing managers, then revised it shortly after the release, then revised it again later in the day. This should remind us that economic gauges are not like measuring a 2×4 stud with a tape measure. Seasonal adjustments and other algorithms are applied to most raw data to arrive at a published figure.
The CWPI index I have been tracking for about a year showed further gains in May, rising up from the winter doldrums. The composite index of the manufacturing and services sectors stands at a bit over 57, solidly in the middle of the strong growth range of 55 to 60. If the pattern holds, we should expect to see this economic gauge rise during the next few months, peaking at the end of the summer.
An average of two key components of the economy, employment and new orders in the services sector, rose back above 55 this month, a level that hasn’t been seen since last October.
**********************
Key Takeaways
The numbers from the labor market are cause for optimism – job gains are rising while new claims for unemployment are falling. Auto sales are strong, an indication that consumers have more confidence. New orders and employment are rising. Weakness in the housing market bears a close watch.