July 3, 2022
by Stephen Stofka
The Atlanta branch of the Federal Reserve maintains a running estimate of current output and other economic indicators updated sometimes daily as reports are released. The app is called EconomyNow and includes GDP, unemployment (UE), retail sales, and inflation. Recent data has caused them to revise their forecast for GDP growth in the 2nd quarter to a -2.1% annualized rate from 0% earlier in the week. Just a month ago, the model was forecasting 2% growth. If there was actually negative growth in the 2nd quarter, that would be two consecutive quarters of negative growth, increasing the likelihood that the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) would call this a recession. However, the BEA does not rely on a single number to call a recession. Let’s look a bit deeper at past recessions.
Out of the many economic reports released each month, the unemployment (UE), inflation and retail sales reports have been reliable predictors of recession. The inflation report is used to adjust retail sales for inflation and produce what are called real retail sales. The combination of positive growth in UE and negative growth in real retail sales is a clear indicator of a weakening economy. The UE report for June will be released this coming Friday, the inflation report on July 13th and retail sales on July 15th.
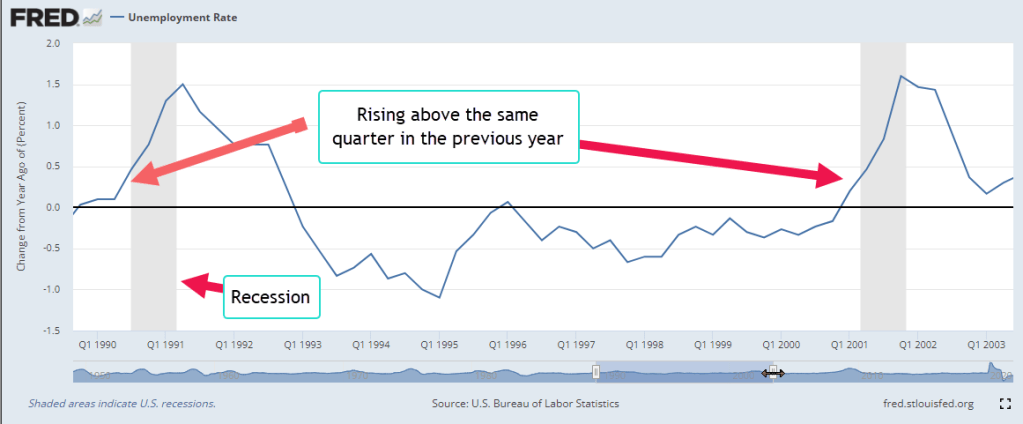
Before each recession, the quarterly average of the unemployment rate rises above that of the previous year. Because the same quarter is compared in both years, the seasonal adjustments and economic flows are similar, an “apples-to-apples” comparison. Look at the rise in UE just before the 1990 and 2001 recessions, shaded gray in the graph below. (I will leave the series identifiers in the footnotes at the end of this post). Notice the hint of a recession in the first quarter of 1996. The Fed had raised interest rates by 3% in the previous year to curb growing inflation, then began lowering them at the end of 1995, averting what might have been a shallow recession.
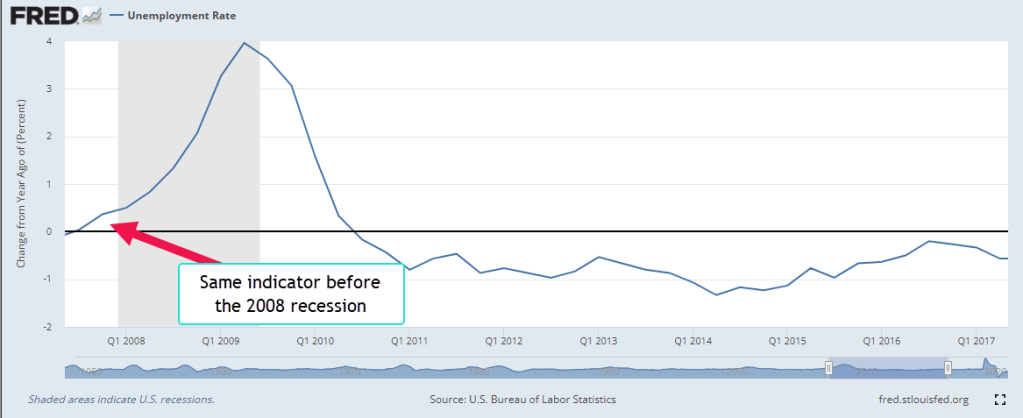
Before the 2007-2009 recession, the growth of UE turned positive.
At the start of 2020, the UE was about the same as it was the previous year, an indication that the economy was susceptible to a shock. The pandemic was the shock of the century.
Let’s add in another indicator, real retail sales, and revisit these periods. When UE growth is positive, state unemployment benefits are rising while income tax revenues are falling. If retail sales are falling, then sales tax revenues are falling as well, putting additional budget pressures on states and localities. 1996:Q1 UE growth had barely turned positive but the growth in real retail sales was still positive and did not confirm the weakness in UE. In 2001, UE growth was positive and real retail growth was negative, confirming the economy’s weakness as investors became disillusioned with the heady promises of the new internet economy.

Before the 2008 recession, UE growth turned positive as real retail sales growth turned negative.

Let’s turn from that historical perspective to our current situation. In the 1st quarter of 2020, these two indicators turned positive and negative because of the pandemic, not in advance of it. At the end of 2019, UE growth was at zero, indicating a weakening economy. However, real retail sales growth was 1.6%.

There is a lot of talk about recession but these two indicators are not confirming that prediction. Growth in real retail sales is still positive and UE growth is negative. The reports in the next two weeks will give us a better picture of recession probabilities. The retail report comes out on July 15th, which is a Friday. The market will react to this report as it does most months. I will update the graph to include both of these indicators in my blog post for July 17th. Have a good 4th celebration and be careful if you live in a western state where it has been dry this year.
//////////////
Photo by Hans Luiggi on Unsplash
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Unemployment Rate [UNRATE], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/UNRATE, July 2, 2022.
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, Advance Real Retail and Food Services Sales [RRSFS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/RRSFS, July 2, 2022.
