On Monday, George finished a re-read of Nassim Taleb’s Fooled By Randomness, an examination of probability without the mathematics. Taleb wrote from the point of view of a market trader but the book contained apt lessons for many kinds of decision making. Mabel went out with a few friends to see the movie Birdman. She asked George if he wanted to go but he was happy to sit around and read.
Taleb told the story of a emerging market bond trader in the 1990s who made a quarter billion dollars for his firm by “buying on the dips.” When the price of the bonds declined, the trader took a highly leveraged long position, betting that the price of the bonds would rally. Each time they did. The man became convinced that he knew this market well. He believed in his own astute judgment. Then came a dip with no subsequent rally. Instead, prices continued to fall. The trader had no stop loss set, a floor price where a trader closes his position to prevent further losses. Instead the trader convinced his bosses at the firm that prices would soon rally. He increased his position as prices fell further. Eventually, prices fell so low that the firm, near bankruptcy, fired the trader and closed the position, losing almost 600 million. George thought about that. There had been one correction in April and May of 2012, a near correction in October and November of that same year. Smaller dips had occurred in June and August of 2013, then in January, April and August of this year. Finally, this month a 7% or so dip. Like the bond trader in the 1990s, the winning strategy of the past few years had been to buy on these dips. The subsequent rise in prices helped convince buyers that their particular view of the market, whether fundamental or technical, was a sound one. Note to self, George thought, don’t confuse good luck with genius.
Earnings and sales reports would drive the market for a few days until Wednesday when the Fed was expected to end its bond buying program. On Thursday, the first estimate of 3rd quarter GDP would be released. After the close Monday, Amgen reported earnings that were 12% better than expected. That would help set a positive mood for Tuesday’s open.
Tuesday’s gauge of consumer confidence from the Conference Board was almost 95, the highest since 2007. Lower gasoline prices have put extra money in consumer pockets. A 25% decrease in the price of gas ($4 – $3) puts about $800 in a consumer’s pocket, a “raise” of almost $20 a week. The declining price of oil caused Chevron to revise its earnings guidance downward by 15-20% for 2014 and 2015 but that was not as bad as anticipated and the shares rose.
The Case Shiller index of home prices in 20 metropolitan areas showed a 5.6% year over year gain, the lowest yearly gain in two years. After almost a decade, the housing market seemed to be returning to more normal patterns of price appreciation.
On the whole, this earnings season seemed positive but the cautionary tone of Taleb’s book reminded George to stay watchful. On Sunday, the European Banking Authority had released the results of their 2014 stress tests on more than 120 European banks. Approximately 20% had failed the test, most of them in Italy, Greece, Cyprus and Spain. When a football game ends, fans leave their seats and move toward the exits in a loosely organized fashion. When a larger bank or sovereign country seems to be in danger of failing or defaulting, investors rush toward the exits as though someone called “Fire!” Still, George was feeling – well, vindicated – that he had seemed to catch this latest dip near the bottom.
The mild weather of late October continued. In shorts and tee shirt, George raked leaves in the backyard on Wednesday morning. Taking a break, he poured himself another cup of coffee, then glanced out the window overlooking the front yard. “Oh, wow,” he muttered. He went to the front door, commenting to Mabel as he opened it, “Must be a bad accident down the street. There’s a Channel 3 van parked across the street. I’m gonna check it out.” If Mabel had a stopwatch, she would have clocked 14 seconds before George was rushing back inside, hurriedly closing the front door. “Geez,” he exclaimed. “What’s wrong?” Mabel asked. “Some woman from the TV station, she starts running across the street toward the house when she saw me! She called my name, for Chrissake!”
George walked into the kitchen, then took up a position on the side of the fridge where he could look out the window onto the street without being seen. “There’s some guy with a video camera with her!” He said, managing to fit anger, annoyance and exasperation into the tone of his voice. Mabel got up from her chair, stood by the living room window, partly concealed by the drapes as she looked out at the street. “What do you think they want, George? Should we go out and talk to them?” “No, that’s the problem. I think that’s exactly what they want – to talk to us. Weird!” Mabel noticed that the rooftop mounted dish on the TV van had been raised up. “I think they’re broadcasting, honey,” she told George in a loud whisper. The woman outside stood on the sidewalk, her back to the house, gesturing, turning to the house, then turning back to the camera man who wielded a shoulder mounted video camera pointed at the woman and George and Mabel’s house. “They wouldn’t come into our front yard, would they?” George wondered aloud. “Isn’t there some kinda law against that?”
Mabel switched channels from the weather to Channel 3. “Oh, no! This is a live feed.” She turned up the volume. The woman reporter standing out on their sidewalk was looking at Mabel from the TV screen. There seemed to be several seconds of delay so that George and Mabel could see the woman reporter gesturing on the front sidewalk, then seeing that same gesture shortly on the TV as though time had fractured.
Reliable source, the reporter said. In advance of the mid-terms, President visited Liscombs, who have not demonstrated active role in politics for either party. Speculation about election strategy in the hotly contested Senate and Governor’s races. A man presumed to be Mr. Liscomb ran back into the house to avoid answering questions. Supposedly independent political organizations spending a lot of money in Colorado. Are the Liscombs bundlers for one of these organizations? Just how independent are these organizations? Why did the President visit this house, this couple? Were campaign rules broken?
George had joined Mabel, standing beside her, staring dumbstruck at the TV. “Are they saying we’re like some kind of political action group like the ones the Koch Brothers fund?” George asked Mabel. “Oh, they’re not saying anything,” Mabel said with a touch of anger. “They’re suggesting, provoking…” she stopped as the report concluded. “Now here comes the tease before the commercial,” she said. “More on the upcoming elections here in Colorado when we come back,” announced the lunchtime news host. “You watch too much TV,” George kidded her. “You’ve gotten hip to their tricks.”
Both of them turned to look outside the living room window. The reporter now stood with the video tech near the rear of the van. “I think they’re leaving,” George said. “No, wait,” Mabel told him. “The dish on the van is still elevated for upload. Wait till they lower it. Then we’ll know they’re leaving.” “Where did you learn all this stuff?” George asked her. “Remember when we had that knife fight at the school five years ago?” Mabel asked. George nodded. “Two kids went to the hospital. The local stations covered it, of course. Got to see the vans. It’s amazing how much equipment they cram in a regular van. There’s probably a third person in the van working all the computers and equipment.”
Eventually, the van pulled away from the curb. George realized that he’d missed the announcement from the Fed on their bond buying program, switched channels to confirm that they had ended the program. Although the Fed had stopped adding to its balance sheet, it continued to hold a whopping $4.5 trillion in assets, the total of the past several years of printing money to support the economy as the country struggled to recover from the Great Recession.
The market closed at the about the same level as Tuesday. Dreamworks, the studio that produced the How to Train Your Dragon movies, reported better than expected earnings after the close, sending the stock up 5% in after hours trading. Kraft also reported earnings slightly higher but the overall sales picture was tepid. Samsung reported a huge 60% decline in profit, squeezed on the high end by Apple and under pressure from mid and low end competitors. The giant insurer MetLife had a blow out quarter. Visa reported better than expected earnings, sending the stock over 4% higher in after market trading.
If Thursday’s first estimate of 3rd quarter GDP growth had come in at 2.5%, below the consensus of 3%, the market could have dropped 2% or more, George thought. Instead, the estimate was 3.5%. The market opened up lower then climbed about 1% during the day.
In each earnings season, there are several stories. One was Gilead Sciences, a small cap biotech firm, whose “killer app” was a new hepatitis drug called Sovaldi. Gilead reported earnings of $1.79 for the past quarter. This was about 10% above earlier guidance but in the crazy world of Wall St., investors had been expecting $1.92, a “whisper” earnings number based on anticipated higher sales of Sovaldi. Instead, sales of the drug were 20% less than the previous quarter. The stock dropped about 5% on Wednesday, before climbing to new highs on Thursday. The stock had more than quadrupled since the beginning of 2012.
On Friday the market jumped 1% at the open. Overnight, the Bank of Japan had announced a massive stimulus program to combat risks of deflation, the bugaboo of all modern economies. If prices might be slightly lower next year, why buy this year? As consumers postpone some purchases, the decline in sales leads to further price declines as companies compete more fiercely to get those fewer sales. Japan’s core CPI, excluding food and energy prices, had risen above 1% in response to earlier stimulus programs but had now fallen in the past several months back toward 1%.
On the domestic front, personal income gains in September were positive, averaging about 2.4% annually and above inflation. Wages and salaries jumped .4%, double the overall income growth. Consumer spending remained tepid, declining to a 1.4% annual pace of growth. Amazon had warned earlier that they expected the Christmas season to be subdued this year. Some speculated that the low rate of inflation and consumer spending would further check any rise in interest rates before the middle of 2015 at the earliest.
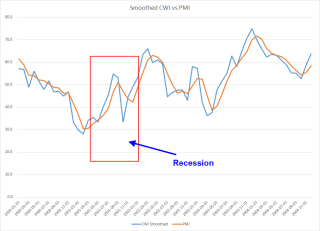
The market closed just slightly above the level it had reached six weeks earlier. George had to remind himself that it was just luck. But he sure felt smart. Then he noticed a disturbing sign, the dragonfly doji after a gap up, on the chart of SPY, the ETF that tracks the SP500 index. The doji are one of many candelestick patterns, a type of technical analysis that tries to understand the psychology of buyers and sellers in the market from price movements over one to three days. After a number of up days, such a pattern might signal that buying pressure has become exhausted. After reading Taleb’s book, George reminded himself once again to be skeptical of signals. The last dragonfly doji after a 1% gap up that George could find in the past few years occurred on April 28, 2012. The market had turned down after that one, losing more than 10% over the following five weeks. Of course, George could have missed some doji simply because the market had not turned after the occurrence of one. As Taleb noted, our view of historical data suffers from hindsight bias, from knowing what happened after a particular event. We can not see the future very well but it’s worse than that. We don’t see the past very well either. George had laughed when he read that.
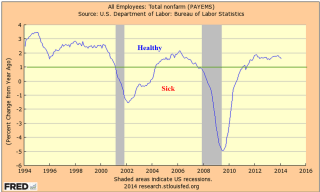
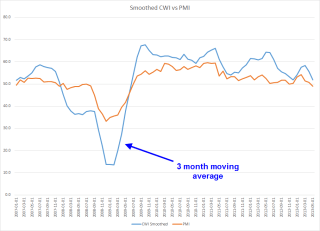
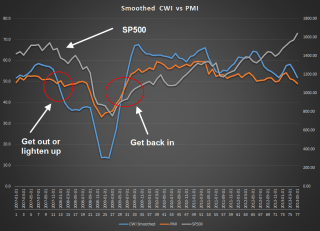
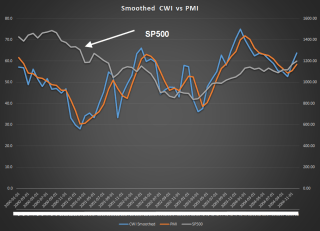
Next week was the first week of the month when several economic reports would capture the attention of investors. The monthly labor report at the end of the week would get the most attention. The ISM indexes of the manufacturing and service sectors would be closely watched for any signs of a slowdown. The sluggish growth in Europe and the strong dollar would have a negative impact on exports, which would show up in the manufacturing index. The CWPI, a composite of both of the ISM indexes, had probably peaked the previous month, and should be lower this month as a natural part of the cyclic pattern of the past several years. Investors could react negatively though to this cyclic decline. The VIX, the volatility indicator, had dropped into a more calm zone and below its 10 day average.
But investors had not abandoned the safety of long-term Treasuries.
If Republicans took control of the Senate in Tuesday’s election, the market would probably get a boost, George figured. The results might not be known for days or weeks if there were recounts in some key senatorial races and that might drag the market down a bit in advance of the upcoming labor report. Would the market go up or down? George could definitely say yes! He looked out the window Saturday afternoon and could tell the direction of one thing for sure – leaves. They were calling to him, or was it his wife with a helpful reminder?