October 19, 2014
On Monday, Mabel met for lunch with several friends, both active and retired teachers, to celebrate a new inductee into the Million Mistake Club. Mabel had once explained it to George, “It started a few decades ago when Mr. Densmore – he taught trigonometry at the school – commented one day in the break room that he had passed the two million mark. He was probably in his late fifties, early sixties at that time. I had only a few years of teaching under my belt at that time and was still trying to get comfortable in the job. Mr. Densmore – funny, I don’t think I ever called him by his first name and I can’t remember what it is right now – anyhow, he just seemed to flow so easily into the job. It was like he wore the job as easily as he wore those old suit jackets he had. Students that I had discipline problems with in my class behaved well in his class. I was still trying to figure out the quiet command thing that can make or break a teacher. He just seemed to make it all look so easy. I asked him what the two million mark was. He said it was the number of mistakes he had made in his lifetime. It didn’t seem possible because it just seemed to me, being fairly new to the job, that he didn’t make any mistakes. Well, except for his taste in clothes. He would sometimes wear brown pants with a gray jacket which seemed to emphasize his age. Mr. Densmore calculated that he made at least a hundred mistakes a day. Joan – she taught sociology – said that no adult could survive if they made that many mistakes in a day. Gary, the biology teacher, said that at the cellular level, our bodies probably made at least that many mistakes a day but we correct most of them before the mistakes turn into cancer or we get sick.”
Mabel had paused then, a catch in her throat. “Anyway, on my 28th birthday, several of the teachers, including Mr. Densmore, chipped in for a catered lunch. Roast beef, some wonderful Italian pastries, potato salad, ice cream.” Mabel paused on her trip down memory lane. “Security in the schools today. Probably couldn’t have caterers come in without some planning weeks in advance.” She went on with her story. “Instead of wishing me a happy birthday, they inducted me into the million mistake club. For the first time in my short career at the point, I felt like I was going to make it. It changed how I taught. I was no longer trying so hard to get everything just right. I would discuss the wrong answers on tests with the students. Why was it wrong? No, Lee was not the general of the union army that won the battle at Gettysburg. But what if Lee had been the general of the union army? How did each army differ and so on. The A students who were good at memorization stretched their imaginations, their analytical skills. The C students started taking more interest in the class, participated more in discussion. The stigma of wrong answers was less. It became more about learning from our wrong answers. I would occasionally take time to review episodes in the history of wrong answers, like phlogiston.”
“What’s that?” George asked. “For a long time people speculated that it was the substance that caused things to burn,” Mabel responded. “Wow,” George nodded. “They didn’t know about oxygen yet. You know, that’s the heart of risk assessment. Learn from our mistakes. The insurance business is just one long rocky path through mistakes in figuring out where the risk is, the degree of risk and how to reduce the risk.”
Monday was the Columbus Day holiday and there wasn’t much good economic news to stem the deepening pessimism in the market. Fears over the spread of Ebola just added to the darkening mood. Mabel would be furious with him if they lost any more money so George sold the two remaining ETFs he hadn’t sold a week or so before. If he had anticipated this pessimism, why hadn’t he bought an ETF that shorted the market? The really good employment report in the beginning of October had made him less sure about his earlier forecast of lower prices. Then he considered – again – buying the 20 Year Treasury ETF but everyone else had been doing that for the past ten days or so and the price was near $121 a share, up about 6% – 7% in the past few week. Geez, George thought. The buying demand for safety has gotta slow down pretty soon.
Tuesday dawned brighter than Monday’s close but then came the release of a report from the International Energy Agency forecasting that oil demand in 2014 would be 22% less than previously forecast. Industrial production in the Eurozone was tepid. George was surprised that the market finished near Monday’s close. Maybe this was the end of the downturn in prices. Like so many retail investors, George had probably sold at the bottom on the previous day. Of little note to the world that day was the fact that George finally cleaned up the wasp nests above the door to the shed. There were only two wasps buzzing around so George didn’t feel like a mass murderer. Where did wasps go for the winter?
On Wednesday morning, George forgot to check the market or economic news before going out to clean up the rock garden. With all of their money now in cash, George had turned his attention to his seasonal chores. The climbing vine had shed most of it’s leaves. The ash tree nearby had shed half of its leaves as well. As George picked leaves out of the ground cover and other perennials in the garden, he wondered whether he should cut down the climbing vines. He had planted them years ago to prevent the neighbor’s dog from jumping the fence during lightning storms in the summer. The dog had died and the vines had spread. Before lunch, Mabel came out onto the back deck. “George, honey. The market is going crazy.” “It’s OK,” George replied, assuring her, “we’re out of the market.” “Oh,” the worry in her voice evaporated. “Well, just thought you’d want to know.” Yeh, just wanted to let me know, George thought wryly. He wondered how many money managers had been fielding calls from clients who were worried about a meltdown like the fall of 2008. “Mrs. Jones, the SP500 is only down about 5 or 6 percent from its September peak,” they might tell their clients. “But I heard that the Dow had dropped 200 points yesterday,” the client might say. To older clients, anything more than 100 points was big. “Yes, but 200 points is just a bit more than 1%. And remember, the Dow is only a part of the stock market.” Yes, the firm is taking prudent care of your money, Mrs. Jones. Put phone down. Next phone call from another worried client.
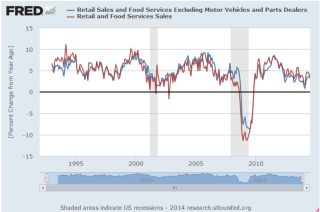
Employment and retail sales are the top two economic reports that consistently set the tone of the market. When the mood is pessimistic, it doesn’t take much negative news to send things into a tailspin. Wednesday’s retail sales report wasn’t bad but it wasn’t good. Strong auto sales in August had led to expectations that total retail sales would decline in September. The decline was just a teeny tiny more than expected, contributing to the wave of selling. The core retail market without auto sales showed 3% year on year growth.
Part of the decline was because gas prices had been falling, producing less revenue. What the market wanted to see was that the American consumer was taking that money saved on gas and spending it on back-to-school items, or a fall wardrobe.
The Census Bureau released manufacturing and trade sales data for August that showed a 4.5% year-over-year increase in sales but a 5.7% increase in inventories. People were not buying as much as distributors were anticipating. This only seemed to confirm fears that growth in consumer spending might be slowing down. As though being routed by an opposing army, traders ran for the rear lines. The SP500 dropped 4% by midday. As George checked quotes on the SP500 ETF, SPY, he saw that it had climbed up from a bottom near 182. He was tempted to put a buy order in, taking advantage of an afternoon rally. Transportation stocks were bouncing up as well. IYT, the iShares ETF, was bouncing off a midday bottom, indicating that money managers were buying in after the 14% decline from the mid-September highs. Then George remembered that he had already tried his hand at these really short term trades. From genius to dunce in a day, he had found that it was not good for him temperamentally. Plus it took an hourly vigilance that he wasn’t willing to give. One more report of Ebola in the U.S. could send this market into a dive within a few minutes. He closed the lid of his laptop. By the end of the day, the Dow Jones had swung more than 600 points. After dropping about 4% during the day, the SP500 closed down only .7% from its previous day close. Fresh troops in the rear had rallied at the end of the day.
Thursday’s release of October’s Housing Market Index from the National Assn. of Homebuilders showed a reversal of six months of rising sentiment. More data from the Eurozone indicated that the entire region might be headed back into recession. Sound the retreat alarm! The market opened up about 1.5% lower. Once again the troops in the rear pressed forward to the battle line as attention turned to several positive reports.
New claims for unemployment were near historic lows, prompting a discussion that had been missing for several years: when would unemployment get low enough to generate some wage growth? George remembered Mabel’s Million Mistake Club earlier in the week. Decades ago, unemployment levels below 5 or 5-1/2% were thought to be inflationary. This target level was called NAIRU, the Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment. At low levels of unemployment, workers could bargain for higher wages which pushed up the cost of products which pushed up prices which led workers to demand more wages, ad infinitum. Like the “law” of gravity, this theory of unemployment and inflation had been regarded as solid by both investors and policy makers. Theories are tested in the passage of time. During the 1990s, unemployment dropped and did not spark inflation. Economists scrambled to explain the phenomenon with global trade adjustments to their models. In the 2000s, unemployment fell below 5% and inflation remained tame by historic standards. More adjustments to the models, more explanations of how the theory was still true. It is still a controversial topic. (1998 article on NAIRU by Nouriel Roubini )
In addition to the positive employment news, Industrial Production grew in September, notching a 1% monthly gain, and rising back into the sustainable growth zone of 4 – 5%, year-over-year.
“Fix Bayonets, men!” came the call as the greenies beat back the morning onslaught from the reds. Greenies were days when the market closed higher than it opened, red the opposite. George wondered if some set or prop designer for CNBC would come up with a Civil War soldier set for the talking heads to play with on camera when the market clash over valuation was particularly intense. As a kid, he’d been so disappointed that all the great battles like the Alamo had already been fought. Santayana’s Mexican legions had rushed forward on the plains of Texas as the small band of brave Texans like Davey Crockett and Jim Bowie prepared for the onslaught. The good ole days when life was exciting – and much shorter.
Friday was the last day of October option trading. The release of new Housing Starts for September, and strong earnings from G.E. and Morgan Stanley prompted a flood of buy orders at the opening bell on Friday. The previous months housing starts had been volatile, rising up strongly in July, then falling a lot in August, and now up more than 6% in September. On a year-over-year basis, September’s starts were up almost 18%.
George was not as awed by the housing data. The declining peaks of year-over-year percent gains in new housing starts would probably continue. Friday’s upswing continued shortly after the open when the latest consumer confidence numbers revealed a rising sentiment based on improvements in employment and lower gas prices. The price had crossed above both the open and closing prices for the past two days. Could be a fake out but George hit the buy button. The earnings season would be in full swing next week.