January 5, 2013 2014
The start of any year presents an opportunity for reflection on the past year as well as the upcoming one. At the start of the year, few, if any, analysts called for such a strong market in 2013. The S&P500 closed the year at 1850, a 30% gain. After a correction in May – June of this year, the index rose steadily in response to better employment data, industrial production, GDP increases, and the willingness of the Federal Reserve to continue buying bonds and keep interest rates low.
I was one of many who were mildly bullish at the beginning of the year but got increasingly cautious as the index pushed past 1600. Yet, month after month came not only positive or mildly positive reports but a notable lack of really negative reports. Leading economies in the Euozone, teetering on recession, did not slip into recession. Fraying monetary tensions in the Eurozone did not explode into a debt crisis. China’s growth slowed then appeared to stabilize. Although the attention has been on the Eurozone the past few years, the sleeping dragon is the Chinese economy, its overbuilt infrastructure, the high vacancy rate in commercial buildings in some areas of the country and the high housing valuations relative to the incomes of Chinese workers.
A year end review is an exercise in humility for most investors. Some fears were unfounded or events unformed which confirmed those fears. People are story tellers – stories of the past, imaginings of the future. An investor who keeps all their money in CDs or savings accounts is predicting an unsafe investing environment for their savings.
Perhaps the best strategy is the one that John Bogle, the founder of Vanguard, advocates. He doesn’t try to predict the future or be the best investor. He aims for that allocation of stocks, bonds and other investments that, on average, forms a suitable mix of risk and reward for his goals, his age and the financial situation of his family. He looks at his portfolio once a year. I do think that a good number of individual investors had adopted the same outlook as Mr. Bogle advocates – until the 2008 financial crisis.
Since the financial crisis, too many investors have adopted a paralyzed strategy, a “deer in the headlight” reaction to the financial crisis that has been hugely unrewarding. Part of this year’s rise in the stock mark can be attributed to individual investors moving cash back into the stock market but I would guess that many of those investors are ready to pull it back out at the first sign of any trouble. This shows less a confidence in the market but a frustrating lack of alternatives.
Long term bond prices took a significant hit in the middle of the year on fears of an impending rise in interest rates. Bond prices had simply become too high, driving down the yield, or return, on the investment. Lower bond yields and meager CD and savings rates provided little return for investors, leaving many investors with little choice but to venture back into the stock market.
*************************************
The Coincident Index of Economic Indicators remains level and strong. A decline in this index below the 1% average growth rate of the population indicates the start of or an impending recession.
Note the index in 2002 – 2003 as it fell back, never rising above the 1% level. I have written about this economic faltering before. Much of the headlines were focused on the lead up to and start of the Iraq war. The recovery from the recession of 2001 and 9-11 was very sluggish. Fears that the country was entering a double dip recession similar to that of the early 1980s prompted Congress to pass the Bush tax cuts in 2003. It was only the increased defense spending of 2003 that offset what would have been a decline in GDP and another recession.
***********************************
A worrisome rise in new unemployment claims has puzzled some analysts. Typically, new claims for unemployment decline at the end of the year, particularly in a year such as this one when reports of strong economic growth have been consistent. Since 2000, rises in claims at the end of the year have been a cautionary note of things to come. Mid-term investors and traders will be paying attention to this in the weeks to come.
However, the decline this year may be more of a leveling process that has been forming for most of the year. On a year over year basis, the long term trend is down – which is up, or good.
In March 2013, I wrote “when unemployment claims go up, the stock market goes down … On a quarterly basis, this negative correlation has proved to be a reliable trading signal for the longer term investor. When the y-o-y percentage change in new unemployment claims crosses above the SP500 change, sell. When the claims change crosses below the SP500 change, it’s safe to buy. ” The percent change in SP500 is still floating above the change in unemployment claims.

**********************************
Sales of motor vehicles in November were above even the most optimistic expectations. The ISM manufacturing index showed a slight decline but is still in strong growth mode and the already robust growth of new orders continues to accelerate. The manufacturing component of the composite index I have been following since last June is at the same vigorous levels of late 1983 and 2003 when the economy finally breaks free of a previous recession. I’ll update the chart when the non-manufacturing report is released this coming Monday.
*********************************
In a healthy economy, the difference between real GDP and Final Sales Less the Growth in Household Debt (Active GDP) stays above 1%, which incidentally is the annual rate of population growth. As the chart below shows, this difference dropped below 1% in late 2007. Finally, six long years later, the difference has risen above 1%, indicating a healthy, growing economy.
**********************************
And now a brief look at the year in review.
At the end of 2012, the price of long term bonds had declined slightly from the nose bleed levels of the fall but there was more to come. I wrote “As this three decade long upward trend in bond prices begins to turn, bond prices can fall sharply as investors turn from bonds to stocks and other investments. We are approaching the lows of interest yields on corporate bonds not seen since WW2. Investors are loaning companies money at record low rates and companies are sucking up all that they can while they can. Sounds a lot like home buying in the middle of the last decade, doesn’t it?”
During the past year, long term bonds declined another 10%. They seem to have formed a base over the past several months. Intermediate term bonds are less sensitive to interest rate changes so they are the safer bet. They lost about 6% in price over the past year. Short term corporate bonds are a good alternative to savings accounts. They pay about 1% above the average savings account and they usually vary very little in price so that the principal remains stable.
At the end of 2012, I wrote “the underlying fundamentals of the economy give reason for cautious optimism.” A month later, “As the saying goes, ‘The trend is your friend.’ When the current month of the SP500 index is above the ten month average, it’s a good idea to stay in the market.” In January 2012, the monthly close broke above the 10 month average. This is a variation of the Golden Cross that I wrote about in January and February 2012.
Let’s look at this crossing above and below the 10 month average. When this month’s close of the SP500 index crosses above the 10 month average of the index, it indicates a clear change in market sentiment. I have overlayed the percent difference between each month’s close and the ten month average.
As you can see, the close near the end of December is near 10% above the 10 month average. If the above chart is a bit too much information for you, here is a graph of the percent difference only.
Is the market overheated? As you can see the market has sustained a robust (or some might call it exuberant) 10% for 6 – 9 months in 2003, 2009, and 2010-2011. From 1994 to 1999, the market spent a lot of time in the 10% percent range. Some pundits are talking about this market as a bubble but we can see that this market has not penetrated the 10% mark. At the end of January 2013, the market closed at more than 7% above it’s 10 month average, over the 4 year positive average of 5.6% (the average when the difference is positive). The market is 20% up since then.
******************************
In March I introduced the “Craigslist Indicator,” the number of work trucks and vans for sale in a local area, as a gauge of the health of the construction industry. It was a funny little indicator that indicated a growing strength in the construction industry at the beginning of the year. Now for the amended version of the Craigslist Indicator: when there are a lot of older work trucks and vans advertised for sale on Craigslist, that indicates a robust construction market.
*****************************
On March 24th, 2013 I wrote ” For the past year, the Eurozone has been in or near recession, yet some are hopeful that increased demand in this country and some emerging markets are helping to balance the contractionary influence of decreased demand in the Eurozone. Let’s hope that this surge in the first part of the year does not fade as it did in 2012.” Instead, emerging markets began to contract and the Eurozone expanded slightly. Investors who bought emerging markets in March 2013 witnessed a more than 10% decline during the summer but the index ended the year at about the same level as nine months ago.
******************************
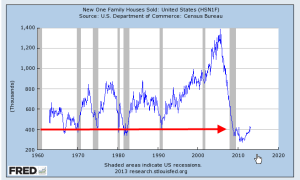
I thought that home prices in the early spring has reached a peak and wrote on March 31st, “The upturn in home prices is still above the trend line growth of disposable income and until personal income can resume or surpass a 3% growth rate, any rise in home prices will be constrained.” The Purchase Only House Price Index (HPIPONM226S) rose steadily throughout the year.
In late summer, I noted the falloff in single family home sales that began in the spring. But prospective buyers were incentivized to make the deal as interest rates began to climb from their historically low levels. Home sales surged upward; a lack of inventory in many cities also formed a support base that propped up prices.

A sobering note in September, “Rising home values are good for those who own a home but increasing valuations make it that much more difficult for buyers trying to buy their first home. People in their twenties and early thirties who are most likely to be first home buyers have been hit hard by the recession.”
*******************************
After a decline in the stock market in June, I wrote “For the long term investor, periods of negative sentiment can be an opportunity to put some cash to work.” Although I took my own advice, I wished I had acted with more conviction. Of course, if the market had declined 10%, I would have been patting myself on the back for my cautious stance. Smiley Face!!
*******************************
In July I noted the rather dramatic decrease in the value of securities held at the nation’s largest banks “Recently rising bond yields have contributed to banks’ operating profit margins but the corresponding value of banks’ bond portfolios has fallen quite dramatically. This decline in asset value affects bank capital ratios, which makes them less likely to increase their lending … [and] will be an impediment to economic growth.” The rising stock market and a respite in the decline of bond prices helped stabilize those portfolios in the second half of the year.
********************************
In September, I noted “Despite all the daily and weekly responses to political as well as economic news, the SP500 stock market index essentially rides the horse of corporate profits.” Profits have more than tripled in the past ten years. We should stay mindful of that stock price to profit correlation as we look out on the investment horizon.
********************************
From time to time I comment on the venality of our elected representatives. Although they might appear to be idle rants to some readers, they are a caution. Politicians make promises to get votes. People become more dependent on those promises. Inevitably, the day comes when the promises can not be met – as promised. Those nearing or in retirement become increasingly dependent on political promises and should leave themselves a cushion – some wiggle room – if possible, when they make income and expense projections. This Washington Post article on proposed budget cuts to military pensions is a case in point. As long as “they” come for the other guy, we don’t pay too much attention – until they come for us. Over the next ten to twenty years, we can expect many small cuts to promised benefits. The cuts have to be small or target a small sector of the population so that they don’t anger voters too much. In several blogs, I have shown how a simple recalculation of the Consumer Price Index eats away at the incomes of workers and retirees. Expect more of these “recalculations” in the future as politicians follow a long standing tradition of making promises to win votes and bargain patronage to gather financial support for their campaigns.
We have the midterm elections to look forward to this year! OK, calm down. Republicans will be hoping to take the Senate and make President Obama’s life miserable for the following two years. I am guessing that the political campaigns for some Senate seats will vacuum in more money than the GDP of a lot of small and poor countries.